The SL (Support Library) command maps function names to library code files.
Syntax

<attributes>
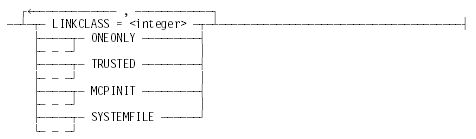
Explanation
SL
Displays the current libraries associated with the various function names. See the CHECKFILE SL command for related information.
SL*
Displays the function names and their attributes. This information is displayed in addition to the library attributes.
SL <function name>
Displays the current library associated with the function name.
SL* <function name>
Displays the current library associated with the function name and the attributes associated with that library. This information is displayed in addition to the library attributes.
SL − <function name>
Does one of the following:
-
If a change is pending for the function, SL - cancels that change. A pending change occurs when you enter the command SL <function name> = <file title> for a ONEONLY function.
-
If the library for the function is not running, the system removes all information for the function from the system tables.
-
If the library for the function is running and is not a ONEONLY function, the system does the following:
-
Changes the library to a temporary library
-
Removes all information for the function from the system tables
-
-
If the library for the function is running and is a ONEONLY function, the system rejects the SL - command with the following response:
CAN'T BE MODIFIED WHILE IN USE
To remove the ONEONLY function with a running library, proceed as follows:
-
Enter the command LIBS to find out the mix number of the library.
-
Enter one of the following commands and wait for the library to terminate:
<mix no> THAW
<mix no> DS
-
Repeat the SL − <function name> command.
When the system removes a function specification, all tasks already linked to the library continue to use the old library. The system creates the following waiting entry message for tasks that subsequently try to link to the function:
FUNCTION <function name> IS NOT DEFINED. DEFINE WITH SL OR DS.
SL <function name> = <file title>
Specifies the library code file that the system is to use for the designated function name. If the function name is already defined, any library attributes associated with the function name are retained. If the function name is not defined (not listed in an SL display), but is defined in the MCP, the MCP automatically assigns attribute values. The system responds as follows according to whether a library for the function is already available (is frozen or has readied an interface) or has been initiated by the library linking mechanism:
-
If a library for the designated function is not currently available or initiated, the system changes the function association as requested.
-
If a library for the designated function is currently available or initiated and if the function is not a ONEONLY function, the system changes the function association as requested, and performs a thaw operation on the old library. Tasks already linked to the old library continue to use it. Tasks that subsequently attempt to link to the function use the new library. The old library resumes and terminates automatically when all old users have delinked, but you can also terminate it with a DS (Discontinue) command.
-
If a library for the designated function is currently available or initiated and if the function is a ONEONLY function, the system changes the function association to indicate that a new library code file is PENDING. If the <file title> refers to the current active code file, and an assignment is already pending, the pending assignment is removed (as if an SL - command had been entered.) Tasks continue to use and link to the old library until the old library resumes or a halt/load occurs. If required, you can terminate the old library with either a THAW (Thaw Frozen Library) command (so that the library will resume when it has no more users) or a DS (Discontinue) command.
If the code file is TADS-compatible and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, the system displays a warning message immediately after the response to the command. If the code file title is placed in a pending state, the system displays the warning message again when the code file replaces the current one and becomes the library file.
SL <function name> = <file title> : <attributes>
Specifies the library code file that the system must use for the designated function name. Sets the attributes associated with the library, as specified. The library attributes are described in the following syntax explanation.
SL <function name> : <attributes>
Sets the attributes associated with the library, as specified, and displays the library associated with the function name.
System libraries which are defined in the MCP have some security attribute values, such as ONEONLY and MCPINIT, that are internally set by the system. For Boolean attributes, such as ONEONLY, MCPINIT, TRUSTED, and SYSTEMFILE, if the attribute is set by the system, it cannot be reset. The linkage class attribute is an integer value in the range 1 through 15, and can be changed only if a new class is able to link to the system-defined linkage class. If an attribute specification violates these rules, the system displays the error message "LIBRARY ATTRIBUTES NOT CHANGEABLE."
The library attributes assigned by the SL command are used only if the library is initiated BYFUNCTION. Otherwise, they are not used.
The library attributes have the following uses:
-
LINKCLASS
An integer value from 0 to 15 that indicates the linkage class to be assigned to the library code file. If the TRUSTED attribute is set, the system determines whether a user can access a procedure exported from a library code file by comparing the linkage class of the user program with the linkage class of the requested library procedure.
If the TRUSTED attribute is reset, the system compares the linkage class of the user program with the linkage class of the entire library code file. Linkage class values for a library code file are as follows.
Class Value
Description
0 (default)
Unprotected. Programs of any linkage class can link to the library.
1
Only programs of linkage class 1 can link to the library.
2 to 7
Reserved for use by system software.
8 to 15
Free for site-dependent definition and use.
Linkage classes of 2 to 5 have been defined as follows.
Class
Type
Classes Allowed to Link to
2
MCS
0, 2, 3, 4
3
Environment Libraries
0, 3, 4
4
Privileged Programs
0, 4
5
Compilers
0, 5
A code file is defined as a privileged program by the PU option of the MP (Mark Program) system command.
The linkage class of a stack is determined at the time the stack is initiated. For a library initiated BYFUNCTION, the linkage class is determined from the LINKCLASS associated with the function name. Linkage classes 4 and 5 are determined from the privileges of the code file.
-
MCPINIT
If set, the library can only be initiated BYFUNCTION by the MCP. The library code file can still be initiated by a PROCESS or RUN construct, or it can be initiated by title as long as the appropriate security considerations for access to the code file are met.
-
ONEONLY
If set, this attribute indicates that only one version of the library code file is permitted to be in use on the system at any one time.
-
SYSTEMFILE
If set, this attribute indicates that the library code file is to be made a nonremovable system file when it is initiated or mapped to a library code file with the SL command.
-
TRUSTED
If set, this attribute indicates that the code in the file is trusted code. This means that the system uses the linkage class assigned to an individual library procedure to determine whether a user program can access that procedure. If this attribute is reset, the system uses the linkage class designated by LINKCLASS to determine whether a user program can access a procedure in the library.
Examples
Example 1
SL
SL GENERALSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/GENERALSUPPORT
SL PLISUPPORT = *SYSTEM/PLISUPPORT
SL PRINTSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT
*SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT/2 (PENDING)
SL USERFUNCTION = (USER)SYSTEM/USERLIBRARYExample 2
SL GENERALSUPPORT
SL GENERALSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/GENERALSUPPORT
Example 3
SL USERFUNCTION = (USER)SYSTEM/USERLIBRARY
FUNCTION "USERFUNCTION = (USER)SYSTEM/USERLIBRARY" ESTABLISHED
Example 4
SL * PRINTSUPPORT
SL PRINTSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT ON DISK
: MCPINIT, TRUSTED, ONEONLY, LINKCLASS=1
TARGET = LEVEL6,
RELEASEID: MCP 17.0 [58.150.000] (58.150.0200)Example 5
SL PRINTSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT/V2
FUNCTION "PRINTSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT/V2"
WILL BE ESTABLISHEDSL PRINTSUPPORT
SL PRINTSUPPORT = *SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT *SYSTEM/PRINT/SUPPORT/V2 (PENDING)
Example 6
SL - USERFUNCTION
FUNCTION "USERFUNCTION" IS NO LONGER ESTABLISHED
Example 7
SL - PRINTSUPPORT
PENDING TITLE FOR "PRINTSUPPORT" IS REMOVED
Example 8
SL USERFUNCTION = SYSTEM/TADSFILE
FUNCTION "USERFUNCTION = SYSTEM/TADSFILE" ESTABLISHED WARNING: FILE IS TADS-CAPABLE
Example 9
SL COMSSUPPORT: -MCPINIT, LINKCLASS=2
LIBRARY ATTRIBUTES NOT CHANGEABLE
Example 10
SL NEWFUNCTION = SYSTEM/NEWFUNCTION : TRUSTED, LINKCLASS = 1
FUNCTION "NEWFUNCTION=SYSTEM/NEWFUNCTION" ESTABLISHED, ATTRIBUTES CHANGED
Considerations for Use
Because the system maintains the function-mapping tables for the library linkage mechanism, a program can access a library through the appropriate function name. The SL command provides the ability to change to new libraries without affecting any running programs or requiring a new library name to be compiled into the calling program.
If you want to copy a new version of a support library to disk and give it the same file name—or otherwise replace the current library with a new library code file with the same name—you must enter an SL command after the new version of the code file has been copied. Whenever a support library is initiated, or whenever the command SL <function name> = <file title> has been successfully executed, the system establishes a link between the library code file currently resident on the disk and the function name. This linkage remains intact even if the code file is subsequently removed or replaced, or if the library is terminated with a THAW (Thaw Frozen Library) or a DS (Discontinue) command. The linkage is broken only under the following circumstances:
-
When the system halt/loads
-
When the disk that contains the code file is closed
-
When you enter a new SL <function name> = <file title> command for the function
A program can access the mapping tables by using the LIBACCESS and FUNCTIONNAME attributes available in ALGOL, Pascal, and NEWP.
Several function names and associated libraries are provided in the system software. For example, many intrinsics reside in the SYSTEM/GENERALSUPPORT library, which has the function name GENERALSUPPORT. All function names suffixed with SUPPORT are reserved for current and future system use. However, the titles of the support libraries can be altered or function names can be created through the SL command.
Access to a support library function can be controlled through the security specifications of the code file for that function.
For ONEONLY support libraries, such as PRINTSUPPORT, the title cannot be changed while the library is running or frozen. Instead, the new title is marked as pending under the function name in the SL function mapping table, and the following response is displayed:
FUNCTION "XXX = YYY" WILL BE ESTABLISHED
The new library is not used until the current library terminates (for example, as a result of a THAW or a DS command) or until a halt/load takes place. You can remove the pending title with the SL − command.
When you use the SL command to assign a code file to a function, the MCP records the function name and the associated code file in its function mapping tables. The MCP becomes a user of the code file until a halt/load or until another SL command maps a new code file to the function name.
If someone replaces the code file-such as by copying in a file with the same name-with another code file of the same name, the change does not become effective until a halt/load or an explicit SL command establishes the new code file as the replacement library.
A program that was previously not executable becomes executable when it has been associated with a function by the SL command and is then initiated by that function.
If security administrator status is authorized for the system, a security administrator usercode is required to execute the form of this command that adds, modifies, or deletes a support library function. If security administrator status is not authorized for the system, any operator, SYSTEMUSER, or privileged user can execute the command.