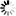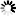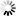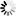The RP (Resident Program) command displays a list of resident programs or marks a code file as resident.
Syntax

Explanation
The resident program designation improves the performance of a program that is run repeatedly. After a resident program has been run once, the segment dictionary stack for its code file remains in memory, even when no tasks are using this stack. Declaring a program as resident increases the amount of memory used in the system when no tasks are using the program; on the other hand, doing so decreases processor and I/O time when the program is reused.
The default status of programs is nonresident.
RP
Lists the file titles of all resident programs currently in memory.
RP <file title>
Marks the code file with the specified file title as a resident program.
RP − <file title>
Cancels the resident status of the code file with the specified file title.
Examples
Example 1
This example lists the file titles of all resident programs currently in memory. The number in parentheses indicates the number of tasks running that program.
RP
----- 3 RESIDENT PROGRAMS ----- (1) *SYSTEM/NEWP ON NI34 (0) *OBJECT/TEST ON PACKGOL ON DISK
Example 2
This example marks the file SYSTEM/ALGOL as a resident program.
RP SYSTEM/ALGOL
SYSTEM/ALGOL IS A RESIDENT PROGRAM
Example 3
This example releases the file SYSTEM/DCALGOL from being a resident program.
RP - SYSTEM/DCALGOL
SYSTEM/DCALGOL NOT A RESIDENT PROGRAM
Example 4
This example attempts to mark the file SYSTEM/ALGOL as a resident program, but the file is not a code file.
RP SYMBOL/ALGOL
WRONG FILEKIND
Example 5
This example attempts to mark the file OBJECT/MISSINGFILE as a resident program, but the system could not find the file.
RP OBJECT/MISSINGFILE
FILE NOT ON DISK