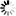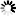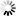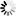The MP (Mark Program) command displays or changes any of a number of options that apply to object code files.
Syntax
── MP ─┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┬─┤
│ ┌◄───────────────── , ────────────────┐ │
└─ <file title> ─┴┬───────────────────────────────────┬┴─┘
├─ + ─<code file option assignment>─┤
└─ - ─<code file option deletion>───┘<code file option assignment>
─┬─ COMPILER ─────────────────────────────────┬────────┤
├─ CONTROL ──────────────────────────────────┤
├─ EXECUTABLE ───────────────────────────────┤
├─ IDENTITY ─┬─────┬─<identifier>────────────┤
│ └─ = ─┘ │
├─ KERBEROS ─────────────────────────────────┤
├─ LOCKED ───────────────────────────────────┤
├─ ONEONLY ──────────────────────────────────┤
├─ PU ─────────────────────┬┬────────────────┤
├─ SECADMIN ───────────────┤└─ TRANSPARENT ──┤
├─ SYSYADMIN ──────────────┤ │
├─ TASKING ────────────────┤ │
├─ <granulated privilege> ─┘ │
├── SERVICE ─┬─────┬─<name>──────────────────┤
│ └─ = ─┘ │
├── SUPPRESSED ──────────────────────────────┤
└── WORKLOADGROUP ─┬─────┬┬─────┬──<name>────┘
└─ = ─┘└─ * ─┘
<code file option deletion>
─┬── COMPILER ────────────────┬────────┤ ├── CONTROL ─────────────────┤ ├── EXECUTABLE ──────────────┤ ├── IDENTITY ─┬──────────────┤ │ └─ * ──────────┤ ├── KERBEROS ────────────────┤ ├── LOCKED ──────────────────┤ ├── ONEONLY ─────────────────┤ ├── PU ──────────────────────┤ ├── SECADMIN ────────────────┤ ├── SERVICE ─┬─ * ──────────┬┤ │ ├─────┬─<name>─┘│ │ └─ = ─┘ │ ├── SUPPRESSED ──────────────┤ ├── SYSADMIN ────────────────┤ ├── TASKING ─────────────────┤ ├── WORKLOADGROUP ─┬─────────┤ │ └─ * ─────┤ └── <granulated privilege> ──┘
<granulated privilege>
─┬── CHANGE ──────────┬────────┤ ├── CHANGESEC ───────┤ ├── CREATEFILE ──────┤ ├── EXECUTE ─────────┤ ├── GETSTATUS ───────┤ ├── GSDIRECTORY ─────┤ ├── IDC ─────────────┤ ├── LOCALCOPY ───────┤ ├── LOGINSTALL ──────┤ ├── LOGOTHERS ───────┤ ├── PLATFORMACCESS ──┤ ├── PLATFORMADMIN ───┤ ├── READ ────────────┤ ├── REMOVE ──────────┤ ├── SETSTATUS ───────┤ ├── SYSTEMUSER ──────┤ ├── UNWRAPRESTRICT ──┤ ├── USERDATA ────────┤ └── WRITE ───────────┘
Explanation
MP
Displays a list of all the allowable code file options.
MP <file title>
Displays the code file options that are set for the specified object code file.
The resident program status of the code file is also shown if the RP system command was used to make the code file into a resident program.
The ALLOWCOMS and ALLOWDMS code file options are also shown if they are set. These attributes can be set only by Unisys. If ALLOWCOMS is shown, the code file can be run by Transaction Server even if the Transaction Server run-time key nnn-TSAPPACCESS-TS is absent. If ALLOWDMS is shown, the code file can open an Enterprise Database Server database even if the Enterprise Database Server run-time key nnn-EDSAPPACCESS-EDS is absent.
<file title> + <code file option assignment>
Sets the specified option of the object code file.
<file title> − <code file option deletion>
Resets the specified option of the object code file.
COMPILER
The COMPILER option specifies whether the object code file has compiler status. Only object code files with compiler status can create other object code files.
If you assign the COMPILER option to an object code file that has TADS capability, and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, a warning message is displayed.
CONTROL
The CONTROL option specifies whether the object code file is a control program. A control program is never scheduled or suspended due to a lack of available memory. Additionally, a control program runs in the same priority category as message control systems (MCSs). This category provides higher priority than WFL jobs or most other types of programs. For a detailed discussion of process priority categories, refer to the System Administration Guide.
If you assign the CONTROL option to an object code file that has TADS capability, and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, a warning message is displayed.
EXECUTABLE
The EXECUTABLE option specifies whether an unsafe object code file is executable.
IDENTITY
The IDENTITY option, if set, associates a message prefix identifier with an object code file. The system adds the specified prefix identifier to all messages produced by that object code file. If you do not set the IDENTITY option, the system adds no prefix identifier to messages displayed by the process.
The identifier that is used as a prefix comes from the code file that causes the system to display a message. For example, if a program with an identity of PROG calls a library with an identity of LIB, any messages that either the system or program produces while it is executing the library procedures are preceded by LIB. Messages that either the system or program produces while it is executing procedures contained in the PROG code are preceded by PROG.
| Note: | The definition of <identifier> requires that it must be enclosed in quotation marks if it includes any special characters. |
KERBEROS
The KERBEROS option, if set, marks the specified program as having the privilege to create, access, and update disk files with the Boolean file attribute KERBEROSACCESS = TRUE.
The system software generation process sets this option for the Kerberos library. This option gives the Kerberos library the privilege to open, read from, and write to the Kerberos KeyTable file. This file contains security-sensitive data that should be accessed only by the Kerberos library.
LOCKED
The LOCKED option specifies whether the program is protected from being discontinued by a DS (Discontinue) or QT (Quit) system command. If the LOCKED option is set and an operator tries to discontinue a program, the system displays a PROGRAM IS LOCKED error message. To discontinue a program that is locked, the operator must first use the <mix number> LP − form of the LP (Lock Program) command, and then enter a DS or QT command.
The LOCKED option of an object code file is inherited by any internal tasks initiated by that object code file. Internal tasks are those resulting from statements that call or process an internal procedure in the object code file.
ONEONLY
The ONEONLY option, if set, prevents more than one process stack from using the object code file.
PU
The PU option specifies whether the object code file is a privileged program. The system allows privileged programs to perform some system functions that would otherwise be denied, such as creating or removing files under another usercode, reading and copying the files of another usercode, and invoking certain operating system control privileges. For further information about the rights of privileged programs, refer to the Task Management Programming Guide.
If you assign the PU option to an object code file that has TADS capability, and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, a warning message is displayed.
Note that the PU option and the PU TRANSPARENT option are mutually exclusive. Refer to the description of the PU TRANSPARENT option later in this subsection.
SECADMIN
The SECADMIN option specifies whether an object code file has security administrator status. Note that the SECADMIN option has an effect only if the system is running Secure Access Control Module security enhancement software. For further information about security administrator status, refer to the Task Management Programming Guide.
If you assign the SECADMIN option to an object code file that has TADS capability, and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, a warning message is displayed.
Note that the SECADMIN option and the SECADMIN TRANSPARENT option are mutually exclusive. Refer to the description of the SECADMIN TRANSPARENT option later in this subsection.
SERVICE
The SERVICE option enables the security administrator to manage a list of security-related attributes for a code file. This option specifies that a program is allowed to use a specific service name as its secure identification.
A code file can be marked to use multiple service names.
When removing a service name from a program, you can use an asterisk (*) to remove all service names associated with that program.
A program marked as a TASKING program (including an MCS) is allowed to use any service name as its secure identification.
SUPPRESSED
The SUPPRESSED option specifies whether processes that are instances of a given object code file are to appear in the output from mix display commands such as the A (Active Mix Entries) system command. If the SUPPRESSED option is set for an object code file, then the operator must add the ALL option to mix display commands to display instances of that object code file in the mix. If the SUPPRESSED option is not set, then such processes are visible in mix display output even if the ALL option is not used.
If a given process becomes suspended, it appears in the W (Waiting Mix Entries) system command display, regardless of whether the SUPPRESSED option of the object code file is set.
SYSADMIN
The SYSADMIN option specifies whether an object code file has system administrator status.
If you assign the SYSADMIN option to an object code file that has TADS capability, and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, a warning message is displayed.
Note that the SYSADMIN option and the SYSADMIN TRANSPARENT option are mutually exclusive. Refer to the description of SYSADMIN TRANSPARENT later in this topic.
TASKING
The TASKING option specifies whether a given object code file has tasking status. Tasking status is a security category that allows the program to perform some system functions that otherwise can be done only by an MCS program. For example, a tasking program can assign a usercode without knowing the password, and can commit some normally fatal task attribute errors without being discontinued. For a complete list of the capabilities of a tasking program, refer to the Task Management Programming Guide.
If you assign the TASKING option to an object code file that has TADS capability, and the system is running with the security option TADSWARN set, a warning message is displayed.
Note that the TASKING option and the TASKING TRANSPARENT option are mutually exclusive. Refer to the following explanation of the TASKING TRANSPARENT option.
WORKLOADGROUP
Assigns or deletes the WORKLOADGROUP code file attribute.
The WORKLOADGOUP code file attribute is used to determine the default value for a task that is initiated with that code file. If the code file attribute has an asterisk (*) prefix, the value overwrites a user-supplied task attribute, and the task attribute cannot be changed.
For example, if you enter
MP MYCODEFILE + WORKLOADGROUP *BATCH
and then
RUN MYCODEFILE; WORKLOADGROUP = INTERACTIVE
the task runs with a WORKLOADGROUP of BATCH.
<granulated privilege>
The <granulated privilege> option specifies whether an object code file has any of the granulated privileges. Setting any granulated privilege option disables the PU option. Setting the PU option disables all granulated privilege options. The USERDATA and IDC options are mutually exclusive of the SECADMIN TRANSPARENT option, and the SECADMIN option is mutually exclusive of the USERDATA TRANSPARENT and IDC TRANSPARENT options. The GETSTATUS and SETSTATUS options are mutually exclusive of the SYSTEMUSER TRANSPARENT option, and the SYSTEMUSER option is mutually exclusive of the GETSTATUS TRANSPARENT and SETSTATUS TRANSPARENT options.
|
Granulated Privilege |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
CHANGE |
A process with this privilege can change the titles of other users' disk files, including the file ownership. However file overwrite is not allowed, unless accompanied by the REMOVE privilege, when a new file name is identical to another user's existing disk file. |
|
CHANGESEC |
A process with this privilege can modify the security file attributes of disk files belonging to other users. |
|
CREATEFILE |
A process with this privilege can create disk files under another usercode without replacing existing files. However, the privilege does not apply to files created through the WFL CHANGE or library maintenance copy operation. |
|
EXECUTE |
A process with this privilege can execute disk files of other users, regardless of their security attributes. |
|
GETSTATUS |
A process with this privilege can use the GETSTATUS intrinsic to retrieve information about jobs, tasks, the status of peripherals, the status of the operating system and mainframe configuration. However, it does not include those GETSTATUS directory and volume requests where privileged-user status is required. |
|
GSDIRECTORY |
A process with this privilege can access GETSTATUS directory and volume requests that are normally restricted to a privileged process. The GSDIRECTORY privilege also provides users with the capability to use the FILEDATA TAPEDIR request. |
|
IDC |
A process with this privilege can update the current DatacomInfo file through DATACOMSUPPORT entry points. |
|
LOCALCOPY |
A process with this privilege can copy files and directories belonging to other users on the local host through library maintenance. |
|
LOGINSTALL |
A process with this privilege can access the MCSLOGGER intrinsic to create log installation records. |
|
LOGOTHERS |
A process with this privilege can access the MCSLOGGER intrinsic to create other log records for which privilege is currently required. Refer to the Events Logged by MCP_LOGGER table in the System Log Programming Reference Manual for information on the log types affected. |
|
PLATFORMACCESS |
A process with this privilege can use the ClearPath Extension Kit for MCP to build and execute image files. |
|
PLATFORMADMIN |
A process with this privilege can use the ClearPath Extension Kit for MCP to have administrative access to the firmware environment. |
|
READ |
A process with this privilege can have read access to other users files, regardless of their security attributes. |
|
REMOVE |
A process with this privilege can remove files belonging to other users. An existing disk file can either be replaced or removed when used in conjunction with either the CREATEFILE, LOCALCOPY, or CHANGE privilege. A close with a purge on a non-owned file also requires the process to have this privilege. |
|
SETSTATUS |
A process with this privilege can use the SETSTATUS intrinsic to control MCP, mix, unit, and operational functions. However, it does not include those SETSTATUS directory and volume requests where privileged-user status is required. |
|
SYSTEMUSER |
A process with this privilege can be specified as a code file privilege using the MP system command. |
|
UNWRAPRESTRICT |
A process with this privilege can use MCP_FILEWRAPPER and MCP_WRAPPER to unwrap wrapped files and containers without hazardous files being marked as restricted. |
|
USERDATA |
A process with this privilege can access the USERDATA intrinsic. This includes all USERDATA functionality available to
|
|
WRITE |
A process with this privilege can have write access to other users disk files, regardless of their security attributes. It can also change all modifiable non-security-related file attributes. |
PU TRANSPARENT
SECADMIN TRANSPARENT
SYSADMIN TRANSPARENT
TASKING TRANSPARENT
<granulated privilege> TRANSPARENT
The TRANSPARENT option is intended primarily for use by libraries. The effect is to make exported library procedures inherit privileges of the programs that call those procedures. Each type of transparent privilege is treated separately by the system. For example, a library object code file might have privileged transparent status, but no security administrator or TASKING status. If a user program with privileged status and security administrator status calls a procedure in that library, the procedure is executed with privileged status, but without security administrator status.
You cannot use privileged transparent status to determine file access rights for a file. These access rights are based only on the object code file in which the file was declared.
For further information about transparent privileges, refer to the Task Management Programming Guide.
Examples
Example 1
The following MP command displays the options that are set for the object code file SYSTEM/GENERALSUPPORT ON DISK:
MP SYSTEM/GENERALSUPPORT ON DISK
FILE SYSTEM/GENERALSUPPORT ON DISK (NEWPCODE) IN USE
PRIVILEGES:
PU TRANSPARENT
SECADMIN TRANSPARENT
GRANULATED PRIVILEGES:
NONE SET
OTHER ATTRIBUTES:
CONTROL
SUPPRESSED
LOCKED
NON-EXECUTABLE: UNSAFE
IDENTITY: GENSUPPExample 2
The following example adds control program status and compiler status to the object code file OBJECT/DELTA. This command also suppresses the object code file from most mix displays, and adds the prefix PROG to messages generated by the program.
MP OBJECT/DELTA + CONTROL, + COMPILER, + SUPPRESSED, + IDENTITY = PROG
Example 3
The following example adds privileged transparent status and security administrator transparent status to the object code file OBJECT/DELTA. This command also removes control program status from the program.
MP OBJECT/DELTA + PU TRANSPARENT, + SECADMIN TRANSPARENT, - CONTROL
Example 4
The following example associates the program named MY/CODE/FILE with the service called MyService. When this program is initiated, it enters the mix with the MyService identifier.
MP MY/CODE/FILE + SERVICE MyService
FILE *MY/CODE/FILE ON DISK (CCCODE)
PRIVILEGES:
PU
GRANULATED PRIVILEGES:
NONE SET
SERVICES:
HADTHISALREADY
MYSERVICE
OTHER ATTRIBUTES:
NONE SETExample 5
The following example removes the association between the program named SYSTEM/PAYROLL and the service named Payroll.
MP SYSTEM/PAYROLL - SERVICE "Payroll"
FILE *SYSTEM/PAYROLL ON DISK (COBOL85CODE)
PRIVILEGES:
PU
GRANULATED PRIVILEGES:
NONE SET
OTHER ATTRIBUTES:
NONE SET
IDENTITY: PAYROLLExample 6
The following example assigns the code file (MYUC)OBJECT/MYCODE with several granulated privileges.
MP (MYUC)OBJECT/MYCODE + READ, + WRITE TRANSPARENT, + USERDATA
FILE (MYUC)OBJECT/MYCODE ON DISK (ALGOLCODE)
PRIVILEGES:
NONE SET
GRANULATED PRIVILEGES:
WRITE TRANSPARENT
READ
USERDATA
OTHER ATTRIBUTES:
NONE SETConsiderations for Use
If the security administrator option has been specified by using the ??SECAD + version of the ??SECAD (Security Administrator Authorization) command, only those users with the security administrator privilege can use the following MP command options:
-
COMPILER
-
EXECUTABLE
-
IDENTITY
-
<granulated privilege>
-
<granulated privilege> TRANSPARENT
-
PU
-
PU TRANSPARENT
-
SECADMIN
-
SECADMIN TRANSPARENT
-
SERVICE
-
TASKING
The MP command affects only instances of an object code file that are initiated after that MP command was issued. Refer to the discussion of privileges assigned to object code files in the Task Management Programming Guide.
You cannot use the MP command on a SYSTEM/ACCESSROUTINES code file while the file is in use.