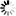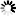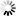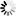The FREE (Free Resource) command detaches resources from the executing partition.
A locking mechanism prevents multiple copies of programs from attempting to use the ACQUIRE (Acquire Resource), CLOSE (Close Pack), FREE (Free Resource), INITIALIZE (Initialize Disk), LB (Relabel Pack), PG (Purge), PG (Purge), and UR (Unit Reserved) commands to access the same device simultaneously. If one of these operations is already in progress when another command is issued to the same device, the command is rejected and the following message is displayed:
PK <unit> <command entered> COMMAND REJECTED BECAUSE ANOTHER COMMAND IS USING THIS UNIT.
If the command is rejected, wait for the current command to complete and enter the command again.
Syntax
── FREE ─┬─ CPM ──<CPM list>────────────────────────────────────┬──┤
│ ┌─◄─────────────── , ───────────────┐ │
├─┴─<device type>──<unit number list>─┴─┬────────────┬─┤
│ └─ :RELEASE ─┘ │
├── NETPORT ──<device number>─ LINEID ─<number>────────┤
└┬─ CHANNEL ─┬─<device number list>────────────────────┘
└─ CHAN ────┘
| Note: | The RELEASE option is valid only for device type PK where PK <unit number> was a non-mirrored single pack family emulated disk prior to being closed. |
<device number list>
A list of numbers or number ranges separated by commas.
Explanation
FREE CPM <CPM list>
The system saves the specified CPMs and marks them user-saved.
<CPM list> is a range of integers from 0-15. In this context, FREE is a synonym for SAVE.
FREE <device type> <unit number list>
FREE <device type> <unit number list> :RELEASE
Detaches the devices from their former group and makes them available to any group. Unit numbers and device numbers can be any integer from 1 to 32767.
The RELEASE option frees and releases the specified emulated disk unit, which puts the associated emulated disk file into the same state as if the MCP was halted. Using the RELEASE option results in the same behavior as FREE without RELEASE when used on an MCPvm system.
-
If you use the RELEASE option, <device type> must be PK and all packs specified in <unit number list> must be non-mirrored, single-pack family emulated disks prior to being closed.
FREE NETPORT <device number> LINEID <number>
Frees the LINEID <number> that is associated with the internal networking port that is identified by the device number. The LINEID number is either 1 or 2, depending on the position of the Ethernet port on which the LINEID depends. This form of the command disables the Ethernet port to be used by networking protocols.
If the LINEID is designated as NEVER ACQUIRE in the Peripheral Configuration Description, the system responds with the following message:
UNABLE TO PERFORM
This message indicates that the system cannot acquire the LINEID.
FREE CHANNEL <device number list>
FREE CHAN <device number list>
Removes the specified channels from the executing partition and makes those paths unavailable for I/O operations.
Examples
Example 1
This example frees a central processing module:
FREE CPM 6
CPM 6 WILL BE FREED
Example 2
This example frees a tape unit:
FREE MT 12
MT 12 WILL BE FREED
Example 3
This example frees a specified channel:
FREE CHAN 5000 CHAN 5000 WILL BE FREED
Example 4
The following examples free the specified channels:
FREE CHAN 5000-5001 CHAN 5000 WILL BE FREED CHAN 5001 WILL BE FREED FREE CHAN 5000,5001 CHAN 5000 WILL BE FREED CHAN 5001 WILL BE FREED
Example 5
The following example frees and releases the specified emulated disk unit, which puts the associated emulated disk file into the same state as if the MCP was halted.
FREE PK 610 :RELEASE PK 610 WILL BE FREED AND RELEASED SUCCESSFULLY FREED PK610 (RELEASED)
Considerations for Use
Attaching a Resource
To attach a resource to an active group, refer to the ACQUIRE (Acquire Resource) command.
Configuring Groups
FREE permanently alters the current definition of the group so that the results of alteration are maintained across halt/loads but not across reconfigurations. The original group definition, whether obtained from the configuration file or through a default configuration, specifies the initial definition of a group. When a reconfiguration command alters the current definition of a group, it does not alter the group definition in the configuration file. You can interrogate the current definition by using the GC (Group Configuration) command.
Identifying Dependent Devices
When the system frees a control device, it marks the dependent devices as having no path. Device x is dependent on device y if freeing y eliminates the only remaining path from x to the executing partition.
Using Critical Units
The following units are critical. If any critical unit is dependent on a control, you cannot free that control.
-
Halt/load family
-
OVERLAY family
-
JOBDESC family
-
CATALOG family
-
SYSTEM/SUMLOG family
Saving Memory
To obtain a successful release of a memory module, consider some or all of the following options:
-
If disk caching is active, either terminate the system caching or downsize the cache area.
-
Assure that adequate overlayable disk space is available.
-
Reschedule the freeing of the memory resource to a time when the system is idle or is not highly active.
-
Wait for the next system halt/load.
-
Issue the SF (Set Factor) system command with the OLAYGOAL option (Factor 1). OLAYGOAL is the percentage of overlayable memory that is to be overlaid on a per-minute basis.
-
Use the CU (Core Usage) system command to monitor memory usage.
-
Issue the HS (Hold Schedule) system command to stop the initiation of any new jobs or tasks.
-
Wait until the tasks terminate to perform the memory save.
-
If necessary, terminate tasks with the DS (Discontinue) system command before you perform the memory save.
Freeing a Disk Pack Associated with the Mirrored Disk Pooling Facility (MDPF)
When you free a disk pack that has been assigned to the free spares pool for a mirrored disk set, the system generates a status change message. When you free each member of a mirrored set of in-use spares, the system generates a status change message. The status change message is defined in the MCP System Interfaces Programming Reference Manual.