The CM (Change MCP) command provides the following capabilities:
-
Displays the status of the MCP on the halt/load pack, on a specified disk family, or on all disk families that contain a halt/load capable MCP
-
Cancels a pending CM action
-
Displays the name of the next MCP to be used, if any
-
Halt/loads the system and changes the current MCP to a permanent or a temporary MCP
-
Converts a temporary MCP to a permanent MCP
-
Alters the status of the current halt/load pack
-
Causes the system to use multiple copies of the MCP
-
Establishes the halt/load capability for a family
-
Alters the status of a family
-
Cancels the halt/load capability of a family
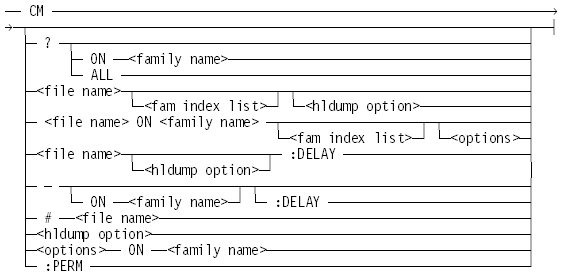
Syntax
<hldump option>

<fam index list>

<options>
Explanation
CM
Displays the name of the current MCP and next MCP, if assigned. If the current MCP is a temporary MCP, the MCP name is displayed as TEMPORARY.
Next MCP refers to a pending MCP specified by CM <file name>, CM # <file name>, or CM <file name> :DELAY.
CM?
CM? ON <family name>
Display the MCP name, creation date, the family indexes on which an MCP was specified in a previous CM command, the HLDUMPDISK setting, and the next MCP to be used. If a delayed MCP is present, that MCP name is displayed. If you do not specify a family, the system displays the information for the halt/load family.
The response to the CM? command also lists the standby halt/load packs of the current halt/load pack. The response to the CM? ON <family name> command lists the standby halt/load packs of the specified pack.
CM ? ALL
Causes the equivalent of a CM? ON <family name> command to be performed for all disk families that contain a halt/load capable MCP (one that has been specified in a previous CM command). In addition to the information normally displayed by the CM? ON <family name> command, the display includes:
-
A heading that specifies the number of families in the display.
-
The family base pack unit number.
CM # <file name>
CM <file name>
Change the operating MCP code file on the current halt/load family to the specified file name. For these commands, the target family is always the current halt/load pack. A halt/load to the new operating system follows.
These forms of the command establish the new MCP code file on the same family member or members that currently have an active MCP code file.
These forms of the command cancel a delayed MCP specified by the command CM <file name> :DELAY.
If you specify the number sign (#), the change in the MCP is temporary. After the initial halt/load to change to the new MCP, any subsequent halt/load makes the system revert to the operating MCP code file in use before you executed the CM # <file name> command.
If the change is temporary, the bootstrap continues to point to the old MCP code file. A subsequent halt/load causes a return to the old operating system. If the change is permanent, the old MCP code file can be removed after the halt/load to the new MCP code file.
After it locates the new MCP code file, the CHANGEMCP process checks for a null mix; if the mix is not null, CHANGEMCP appears in the list of waiting entries. The waiting MCP change is called a pending change. (Libraries such as GENERALSUPPORT do not constitute mix entries.) In contrast, the primitive version of the CM command (??CM) does not wait for a null mix count. Refer to the ??CM (Change MCP) command.
| Note: | It is usually difficult or impossible to terminate every task
and job in the mix. Therefore, it is usually mandatory that you use
the primitive version of the CM command (??CM) to change the
executing MCP. But the primitive ??CM command does not have
all the features of the normal CM command. For example, the primitive
??CM command does not allow you to use the index list option. When
you need to invoke one of these special features, proceed as follows:
|
CM −
Cancels a pending MCP change.
CM − ON <familyname>
Remove halt/load capability from a family or specific members of that family (the index units). The system locates the MCP code file (and any duplicate MCP code files) and resets the system file bit for each of these files. If the family is a standby halt/load family, the system implicitly removes that status. If the family has a delayed MCP, the system removes the reference to the delayed MCP.
CM − ON <family name> :DELAY
Removes the reference to the delayed MCP from the specified family.
You might want to use this form of the command when you have established a delayed MCP on a family. Then, rather than performing a halt/load operation on that family, you used the HLUNIT command to switch to another halt/load family and subsequently halt/loaded it. However, the delayed MCP is still linked to the original unit.
Using the CM − ON <family name> :DELAY form of the command delinks the delayed CM from the original family.
CM <file name> ON <family name>
Creates a family with halt/load capability with the indicated code file. The target family is specified by the family name. The current halt/load pack cannot be specified in this command.
Use this form of the CM command to establish halt/load capability for a family. To start up on the new MCP, use the HLUNIT (Specify Halt/Load Unit) command to designate the unit as the new halt/load family, and then perform a manual halt/load.
If you have not performed a CM command on the designated family, this form of the command puts the new MCP code file on the base pack of the designated family. If you have previously performed a CM command on the designated family, this form of the command establishes the new MCP code file on the same member or members of the family that the previous command did.
When you create a family with halt/load capability, you must copy SYSTEM/KEYSFILE to that family, and re-copy the file when it is updated as the result of an IK (Install Keys) command. The MCP uses the keys file on the halt/load family, and absence of run-time keys might result in programs failing to run, and security options being reset.
CM <file name> : DELAY
Sets the specified code file as a delayed MCP. The code file is used whenever the system is forced to halt/load. The code file is loaded as a temporary MCP and can become the permanent MCP after the system is running.
CM – : DELAY
Removes the reference to the delayed MCP.
CM : PERM
Transforms the current MCP from a temporary MCP to the permanent MCP by updating the bootstrap to point to the new MCP. This version of the command is valid only when used on a temporary MCP (for example, CM #).
<fam index list>
Specifies duplicate MCPs on the specified members of a multipack family. In the past, these duplicate MCPs were used if a disk error occurred when reading in MCP code or data from the base MCP. However, these copies are no longer referenced because all MCP code and data is read in permanently during initialization. The CM command now issues an RSVP message to this effect. If you continue to use the family index list, observe the following guidelines:
-
The list cannot contain duplicate numbers.
-
If you specify a list and direct the CM command to the current halt/load pack, you must include in the list the family index of the current halt/load pack.
-
Each unit referenced in the command must be suitable for use as a base pack. That is, the unit must be either a base pack or a continuation pack with a duplicate directory. Refer to the DD (Directory Duplicate) command. Otherwise, the message “CM INVALID OR MISSING DISK” appears.
-
When you specify a family index list, the system cancels the delayed MCP on that family.
When the system is running with duplicate MCPs, it adds to the file name a suffix of the form FMLYINXnnn, where nnn represents the three-digit family index number of the member on which the code file resides.
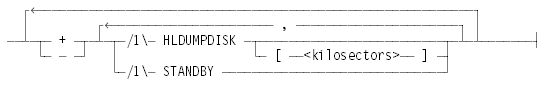
<options>
The following options apply to the CM command:
-
+ HLDUMPDISK
Causes the system to search the specified family for a SYSTEM/HLDUMPDISK/<nnn> file. If the system finds one, it verifies that the file is a usable dumpdisk file. If the system does not find a usable SYSTEM/HLDUMPDISK/<nnn> file, it creates one. If you include a [<kilosectors>] specification, the new file has the specified capacity. Otherwise, you must supply the desired capacity for a new dumpdisk file in response to an AX (Accept) message.
When the + HLDUMPDISK option applies to the current halt/load family, the SYSTEM/HLDUMPDISK/<nnn> file immediately becomes a dumpdisk file in use.
If you have enabled dumpdisk capabilities through both the DN (Dump Name) and CM + HLDUMPDISK commands, the system uses the HLDUMPDISK file for dumps that occur during system initialization and then uses the file named in the DN command for subsequent dumps.
The CM + HLDUMPDISK command cannot direct a dumpdisk file to a mirrored set or to a family containing a mirrored set. If you make such an attempt, the system returns an error message.
-
– HLDUMPDISK
Immediately removes the SYSTEM/HLDUMPDISK/<nnn> file from use.
For more information about dumpdisk files, refer to the DN (Dump Name) command.
-
CM + STANDBY ON <family name>
Causes the specified family to become a standby halt/load family for the current halt/load family. The specified family must already be a halt/load capable family.
Whenever data such as configuration information or the mirror information table (MIT) is preserved on the halt/load family, that data is also preserved on all online standby halt/load families of the current halt/load family. An example of configuration information data is the FREE/ACQUIRE/UR/UR status of units and data link processors (DLPs), disk locations (DLs), support libraries (SLs), memory disk, disk cache specifications, and the backup of settings stored in the JOBDESC file. In this way, all the information transferred to the target families during the execution of the original CM <file name> ON <family name> command is kept continuously up to date. The information on online standby halt/load family is always current. If the current halt/load family fails, one of its standby halt/load families can be used without concern as to when a CM operation was last performed on it.
Note that although disk location (DL) specifications are kept up-to-date on all online standby halt/load families, the files located by way of these specifications (such as backup files, log file, and JOBDESC file) are maintained only on the specified families.
When you create a standby halt/load family, you should copy SYSTEM/KEYSFILE to that family, and recopy the file when it is updated. The MCP uses the keys file on the halt/load family, and absence of run-time keys can result in security options being reset. When these options are reset, they are also reset on all other standby halt/load families.
The system preserves a self-inclusive list of standby halt/load families on the current halt/load family and on its standby halt/load families. Thus, if you make B a standby halt/load family for A, A automatically becomes a standby halt/load family for B.
If the system does not find a given standby halt/load family for the current halt/load family after a halt/load, its specification remains in the list of standby halt/load families. The system issues the following message: STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name> NOT FOUND. Failure to respond to this RSVP message does not delay completion of system initialization.
The response to a CM? command indicates the offline status of these standby halt/load families. If the status of the standby halt/load family changes to online and the unit is still halt/load capable, the system updates it so that its preserved data structures are current, and the family remains a standby halt/load family for the current halt/load family. If the status of the standby halt/load family changes to online but the family is not halt/load capable, the system removes it from the list of standby halt/load families for the current halt/load family. The system issues the following message:
NO MCP FOUND ON STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name>. IT WILL NOT BE UPDATED.
You can close a standby halt/load family for the current halt/load family and place it in the same offline state described in the previous paragraph; the system does not delete it from the standby halt/load families for the current halt/load family.
-
CM <file name> ON <family name> + STANDBY
Causes the specified family to be made halt/load capable and to become a standby halt/load family for the current halt/load family. (If you do not specify + STANDBY, the specified family does not become a standby halt/load family at the end of the operation, whether or not it had been at the start.)
-
CM – STANDBY ON <family name>
Causes the specified family (which must already be a standby halt/load family ) to no longer be a standby halt/load family. The specified family remains halt/load capable. The specified family must already be a family with halt/load capability.
Examples
Example 1
This example displays the name of the next MCP.
CM
MCP: *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170 Next MCP: *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170A
Example 2
This example changes the MCP code file on the current halt/load family to the specified file name. However, the change in the MCP is only temporary. After the initial halt/load to change to the new MCP, any subsequent halt/load makes the system revert to the previous MCP code file that was in use.
CM # SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170B
SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170B NEXT MCP, MEMONLY
Example 3
This example changes the MCP code file on the current halt/load family to the specified file name
CM SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170B
SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170B WILL BE THE NEXT MCP
Example 4
This example produces a display of the MCP name, creation date, family indexes on which an MCP was specified in a previous MCP command, and the HLDUMPDISK setting. This information is applicable to the halt/load family.
CM ?
CM STATUS :
MCP : *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP53170 ON DISK
CREATION DATE : Monday, March 3, 2008 (2008063)
CM'ED MCP ON FAMILY INDEX : 1
HLDUMPDISK : SET Example 5
This example shows the display for a CM query. Notice that a delayed MCP is listed.
CM?
CM STATUS :
MCP : *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP53170 ON DISK
CREATION DATE : Monday, March 3, 2008 (2008063)
CM'ED MCP ON FAMILY INDEX : 1
HLDUMPDISK : SET
DELAYED MCP: *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP/53170C
Example 6
This example produces a display of all disk families that contain a halt/load capable MCP.
CM ? ALL
CM STATUS : (2 CM'ED FAMILIES)
MCP : *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP53170 ON DISK
BASE PACK : (PK500) (CURRENT HALT/LOAD FAMILY)
CREATION DATE : Monday, March 3, 2008 (2008063)
CM'ED MCP ON FAMILY INDEX : 1
HLDUMPDISK : RESET
STANDBY HALT/LOAD UNITS:
HLSTANDBY (PK501) (ON-LINE)
DELAYED MCP: *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP53170D
MCP : *SYSTEM/DELTA/MCP53170 ON HLSTANDBY
BASE PACK : (PK501)
CREATION DATE : Monday, March 3, 2008 (2008063)
CM'ED MCP ON FAMILY INDEX : 1
HLDUMPDISK : SET
STANDBY HALT/LOAD UNITS:
HLSTANDBY (PK500) (CURRENT HALT/LOAD UNIT)Example 7
This example creates a halt/load DUMPDISK file on the halt/load family.
CM + HLDUMPDISK
CM OPTIONS WILL BE CHANGED
Considerations for Use
Using Duplicated or Triplicated MCPs
If you want to use duplicated or triplicated MCPs on your system, the CM procedure needs two or three copies of the MCP code file each time you change MCPs. You can use either of the following methods to create duplicated or triplicated copies of the MCP code file:
-
You can supply one copy of the MCP code file, and the CM procedure produces the extra copies that are needed and gives them names that include FMLYINX<nnn>. The chief disadvantage of this method is loss of profitable system time while the CM procedure is running, the rest of the system is idle.
-
You can make two or three copies of the code file yourself before you execute the CM command. The disadvantage of this method is that it is more difficult to make the copies correctly.
If the CM command is for the current halt/load family, to ensure that the CM command takes effect, perform the following sequence of steps:
-
Enter the following command:
CM <file name> <family index list>
The system displays the following message:
CM PENDING, WAITING FOR NULL MIX
-
Enter the following primitive command to force the process to proceed without waiting for the null mix:
??CM <file name>
Allowing the CM Procedure to Copy the MCP Code File
To let the CM procedure generate the extra copies of the MCP code file, perform the following steps:
-
Copy the MCP code file to the halt/load family or the family for which you want to issue the CM command.
-
Issue the CM command with the file name and the index unit list of the family members that are to receive the duplicated copies of the MCP code file.
The command syntax for the halt/load family is as follows:
CM <file name> (<family index list>)
The command syntax for the standby families is as follows:
CM <file name> ON <family name> (<family index list>)
Copying the MCP Code File Yourself
To make the extra copies of the MCP code file yourself, perform the following steps:
-
Make a copy of the MCP code file that is to be duplicated or triplicated onto each member of the family in the index unit list. Use the following syntax:
COPY <file name> AS <file name>/FMLYINX<nnn> TO <family name> (PACK,FAMILYINDEX=<nnn>)The variable nnn is the 3-digit family index number of one of the members of the family in the index unit list that is to receive a copy of the MCP code file.
-
Repeat step 1 for each member that is to receive a copy of the MCP code file. Be sure to change nnn appropriately in both places in the COPY statement.
-
Issue the CM command and specify one of the new names in full with the index units list.
The command syntax for the halt/load family is as follows:
CM <file name>/FMLYINX<nnn> (<family index list>)
The command syntax for the standby families is as follows:
CM <file name>/FMLYINX<nnn> ON <family name> (<family index list>)
Using CM? to Find Out if a Pack Can No Longer Be Halt/Loaded
If a REPLACE (Replace Pack Volume) command finds bad sectors or if you perform a DD – command on a halt/load capable pack, the pack is no longer halt/load capable. The REPLACE and DD – commands do not result in any warnings, but you can use the CM? command to find out if the family is no longer halt/load capable.
The following error messages can be generated both by the CM command and during subsequent halt/loads when the standby halt/load feature is active.
-
MCP ON STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name> TOO OLD. IT WILL NOT BE UPDATED.
The CM command is applied to the specified family that contains an MCP that is too old to correctly interpret the structures in use by the current MCP. The specified family remains in the list of standby halt/load families for the current halt/load unit, but its structure is not updated. In the response to the CM? command, the specified family is flagged with the following phrase:
[[[ MCP INCOMPATIBLE ]]]
The most common occurrence of this message is upon the first CM to a new MCP software release level. It indicates that the system on the specified family is several software release levels older, and must be replaced by an MCP with a more recent software release level.
-
STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name> NO LONGER CMED. IT WILL BE DELETED FROM LIST.
The specified family is no longer halt/load capable. It will be deleted from the list of standby halt/load units for the current halt/load unit.
-
NO MCP FOUND ON STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name>. IT WILL NOT BE UPDATED.
The specified family is halt/load capable, but no MCP was found on it. The specified family remains in the list of standby halt/load units for the current halt/load unit, but its structures are not updated. In the response to the CM? command, the specified family is flagged with the following phrase:
[[[ ERROR ]]]
Input/output (I/O) errors or data structure inconsistencies on the specified family can cause this situation. Also, there is a sequence of DD and CM commands that produces a family with halt/load capability with no MCP.
-
ERROR IN STRUCTURES ON STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name>. IT WILL NOT BE UPDATED.
Input/output (I/O) errors or data structure inconsistencies were encountered while the preserved structures were being located on the specified family, or I/O errors were encountered while these structures were being preserved. The specified family remains in the list of standby halt/load families for the current halt/load family, but its structures are not updated. In the response to the CM? command, the specified family is flagged with the following phrase:
[[[ ERROR ]]]
-
STANDBY H/L UNIT <family name> NOT FOUND.
The specified family was not found during the system initialization following the most recent halt/load. The specified family remains in the list of standby halt/load families for the current halt/load family. In response to the CM? command, the specified family is flagged with the following phrase:
[[[ OFF-LINE ]]]
-
WARNING: <family name> IS NO LONGER AN ONLINE STANDBY H/L UNIT.
The specified family has been deleted from the list of standby halt/load families for the current halt/load family as the result of a CM, PG, or RC command, or was taken offline by the CLOSE command. In the latter case, the specified family remains in the list of standby halt/load families for the current halt/load family, but its structures are not updated. In the response to the CM? command, the specified family is flagged with the following phrase:
[[[ OFFLINE ]]]
-
PK<unit number> IS NOT A STANDBY H/L UNIT.
The command CM – STANDBY ON <family name> was entered, but the specified family does not contain a list of standby halt/load families.
-
PK<unit number> IS NOT CMED.
The command CM + STANDBY ON <family name> was entered, but the specified family is not halt/load capable.