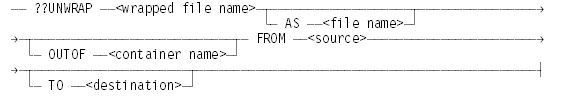
The ??UNWRAP (Unwrap Files) command unwraps a single wrapped file or a file within a wrapped container from a CD-ROM or disk without the use of the WFL compiler.
A container is a file containing other files in an encoded form, suitable for transport across an open network to another host. You can use the WRAP statement in WFL to create single wrapped files or wrapped containers containing multiple files. You can later use the UNWRAP statement in WFL to recreate original files from single wrapped files or wrapped containers on the destination host.
The ??UNWRAP primitive command supports only a subset of the syntax of the WFL UNWRAP statement. The ??UNWRAP primitive is intended for use when the WFL compiler is missing or fails to freeze.
Syntax
<source>
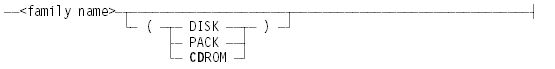
<destination>
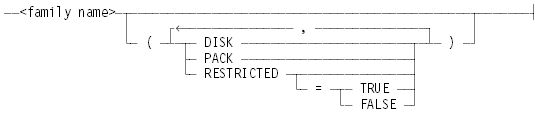
<container name>
<wrapped file name>
These elements follow the <file name> syntax.
Explanation
??UNWRAP <wrapped file name> . . .
Creates an unwrapped file based on the specified wrapped file. By default, the file is created under the same usercode as the wrapped file upon which it is based. (Note that containers can include files with a variety of different usercodes.)
The remaining options are described separately below.
AS <file name>
Creates the unwrapped file using the specified file name, instead of the original file name.
If the specified file name includes a usercode, the file is created under that usercode. Otherwise, the file is created under the same usercode as the wrapped file.
If the AS <file name> clause is omitted, the file is recreated under the same name as the wrapped file.
OUTOF <container name>
Specifies that the unwrapped file is to be created from a wrapped file in the specified container.
If the OUTOF <container name> clause is omitted, the system treats <wrapped file name> as a reference to a single wrapped file instead of a file within a wrapped container. If the AS <file name> clause is also omitted, the recreated file has the same file name as the wrapped file, and overwrites the wrapped file.
FROM <source>
Specifies the disk or CD-ROM where the single wrapped file or container resides. The FROM <source> clause is required. The default <source> is DISK.
TO <destination>
Specifies the disk family where the file is to be created.
If the TO <destination> clause is omitted, the system creates the file on the family named DISK.
Examples
Example 1
The following command creates the file (THP)RECIPTS/INCOMING ON LFPACK, based on the single wrapped file (THIEN)RECEIPTS/FILE ON DISK:
??UNWRAP (THIEN)RECEIPTS/FILE AS (THP)RECEIPTS/INCOMING FROM DISK TO LFPACK(DISK)
Example 2
The following command creates the file (THIEN)RECEIPTS/MONDAY ON DISK from the wrapped file of the same name in the container (THIEN)RECEIPTS/FEBRUARY ON LFPACK:
??UNWRAP (THIEN)RECEIPTS/MONDAY OUTOF (THP)RECEIPTS/FEBRUARY FROM LFPACK(DISK)
Example 3
The following command creates the file (THP)ACCTS/MONDAY ON LFPACK from the wrapped file (THIEN)RECEIPTS/MONDAY in the container (THIEN)RECEIPTS/FEBRUARY ON DISK:
??UNWRAP (THIEN)RECEIPTS/MONDAY AS (THP)ACCTS/MONDAY OUTOF (THIEN)RECEIPTS/FEBRUARY FROM DISK TO LFPACK(DISK)
Considerations for Use
If the security option RESTRICTUNWRAP is set, object code files that are unwrapped are marked as restricted. To prevent the unwrap process from restricting the object code files, reset the security option RESTRICTUNWRAP or use the RESTRICTED = FALSE specification. Refer to the MCP Security Overview and Implementation Guide for more information on the SECOPT system command and the RESTRICTUNWRAP option.