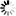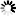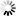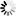The AT (At Remote Host) command directs a system command to another host in the network. Any response to the command appears at the ODT at which the command was entered.
Syntax

Explanation
The content of the remote system command is not checked for syntax at the local host, but is transferred to the remote host. The command syntax must conform to the operator command language of the remote host and must not violate any security or access control restrictions that are in effect at that host.
The local host name can be used in an AT command if the remote system command is NW (Network Prefix). If any other remote system command used, an error is displayed.; you should resubmit the command without the AT <hostname> prefix.
.
The remote host response to the AT command is restricted to a maximum of 255 lines. If the output is truncated, then the following message is appended to the response:
*** RESPONSE TRUNCATED ***
Examples
Example 1
AT BLUE W
***********REPLY FROM BLUE****************
-Job-Task-Pri---Elapsed--- 1 WAITING ENTRY --------------- 1566/1568 50 1:10 *SYSTEM/DUMPANALYZER ON HLDISK NO FILE MEMORY DUMP (MT) #1
Example 2
AT BLUE J
***********REPLY FROM BLUE*****************
-Mix-Pri---------------- JOB ENTRIES ---------------------- 1566 50 JOB BEGIN JOB;RUN *SY 1568 50 *SYSTEM/DUMPANALYZER ON HLDISK
Example 3
AT BLUE 1568 FA TITLE=(USER)A ON DISK
**********REPLY FROM BLUE*****************
NO RESPONSE GENERATED
Considerations for Use
Host Services permits access to systems that are part of either a BNA or an OSI network.
The response from the remote host uses the language and conventions defined by the LANGUAGE and CONVENTION system options of the remote host. For more information about the LANGUAGE and CONVENTION attributes, refer to the SYSOPS (System Options) command and to the MultiLingual System Administration, Operations, and Programming Guide.
With each system command sent to another host, HOSTSERVICES provides a usercode that the host can use to satisfy its security or access control restrictions. If the command is entered at an ODT to which a terminal usercode was assigned (refer to the TERM (Terminal) command), that usercode is used. If the command is entered through the DCKEYIN interface, the usercode of the program is used. Otherwise, the host usercode is used. If there is no terminal usercode or host usercode, an error occurs and the AT command cannot be used. Refer to the HU (Host Usercode) command.
When a system receives a system command from a remote host, it determines whether the command came from a usercode defined as a SYSTEMUSER. A remote user whose usercode is marked with the SYSTEMUSER attribute has the same ODT capabilities as the ODT operator on the local system.
Any remote user can enter Work Flow Language (WFL) jobs. When the system command containing the job is received, the local alias usercode of the usercode used to transfer the job is examined. If the local alias usercode is marked as a SYSTEMUSER, the job runs without a usercode; otherwise, it runs under the local alias usercode. If the job contains a usercode, it runs under that usercode.
A remote user who is not a SYSTEMUSER can use the following system commands to monitor jobs and tasks running under that usercode.
|
Command |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
A |
Active Entries |
|
AX |
Accept |
|
BADFILE |
Bad File |
|
C |
Completed Mix Entries |
|
CU |
Core Usage |
|
DBS |
Database Stack Entries |
|
DS |
Discontinue |
|
DUMP |
Dump Memory |
|
FA |
File Attribute |
|
FR |
Final Reel |
|
HI |
Cause EXCEPTIONEVENT |
|
J |
Job and Task Display |
|
LIBS |
Library Task Entries |
|
MSG |
Display Messages |
|
MX |
Mix Entries |
|
NF |
No File |
|
OF |
Optional File |
|
OK |
Reactivate |
|
OT |
Inspect Stack Cell |
|
RM |
Remove |
|
S |
Scheduled Entries |
|
SQ |
Show Queue |
|
ST |
Stop |
|
THAW |
Thaw Frozen Library |
|
TI |
Times |
|
W |
Waiting Entries |
|
Y |
Status Interrogate |
In addition, a remote user who is not a SYSTEMUSER can also use the following commands to display the status of the system.
|
Command |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
CS |
Change Supervisor |
|
CU |
Core Usage |
|
HOSTNAME |
Host Name |
|
ID |
Initialize Data Comm |
|
MM |
Memory Module |
|
SC |
System Configuration |
|
SI |
System Intrinsics |
|
SL |
Support Library |
|
TD |
Time and Date |
|
WM |
What MCP |
A task named ODT/HANDLER handles the transfer of system commands and responses between hosts. HOSTSERVICES automatically starts ODT/HANDLER after receiving an AT command on the local host or an ODT request from a remote HS host. The ODT/HANDLER is an independent runner that terminates automatically when Host Service operations are terminated or when no system commands are sent to or received from other hosts for five minutes.