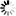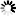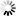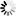The CACHE (Disk Cache) system command controls the cache memory status of disks, displays cache statistics for the entire system, and dynamically resizes the amount of memory allocated to the disk cache.
Syntax
── CACHE ─┬─────────────────────────┬─────┤
├─ + ─┬─ PK ──<unit list>─┤
├─ - ─┘ │
└─ MEMORY ──<cache size>──┘<cache size>
─┬─ <megaword limits> ─┬─────────────┤ └─ <gigaword limits> ─┘
<megaword limits>
── <integer between 4 and 262144> ─┬─ MEGAWORDS ─┬──────┤
└─ MWORDS ────┘<gigaword limits>
── <integer between 1 and 256> ─┬─ GIGAWORDS ─┬───────┤
└─ GWORDS ────┘Explanation
CACHE
Displays the following information:
-
The number of disk units that are currently under the control of the disk caching subsystem
-
The ratio of disk cache read hits to cache requests for all cached disks within the last sampling interval
-
Disk cache memory size
-
The total number of cache requests for all cached disks within the last sampling interval
-
The overall data transfer rate of data for all cached disks within the last sampling interval
-
Traffic statistics for each cached disk within the last sampling interval
CACHE + PK <unit list>
Starts caching for the specified units.
CACHE − PK <unit list>
Stops caching for the specified units. This command also stops maintaining the disk cache statistics for the specified units.
CACHE MEMORY <cache size>
Dynamically resizes cache memory.
If <cache size> is less than the current size of the memory allocated to the disk caching subsystem, the amount of memory allocated to the disk caching subsystem is decreased to <cache size>. Setting the <cache size> to zero suspends disk caching.
If <cache size> is greater than the current size of memory allocated to the disk caching subsystem, the amount of memory allocated to the disk caching subsystem is increased to <cache size>.
When increasing the disk cache, the MCP does not allow the system memory size to fall below the minimum size defined for the system.
The resizing of disk cache memory usually takes place immediately. Under some circumstances, however, areas marked as "save memory" can prevent the size of disk cache memory from being increased. In this case, a halt/load is required for the request to occur. As a result, a waiting entry appears with the following RSVP:
Unable to resize disk cache memory. Responses are DS (Give up), AX DEFER (Resize cache next haltload), or AX HALTLOAD (Haltload and resize cache now).
Examples
Example 1
CACHE
Disk Caching Statistics:
Caching Packs = 35
Overall ReadHits/Requests:76% Cache Size:10 Mwords
Cache: 70 Reqs/Sec 336 Kbytes/Sec
% % %
Reqs/ Rhit/ Read/ Rhit/ Kbytes/
PK Sec Read All All Sec
165 SYSTEM #1 2 75 23 17 5
166 CAE #1 1 100 44 44 1
176 DISK #1 6 100 49 49 5
184 PACK #1 3 23 96 22 38
185 X3 #1 3 94 72 67 7
187 BDRIVE #1 55 97 100 97 280The CACHE command displays the following items:
-
Caching Packs
The number of online packs you are currently caching. Each cached mirrored set counts as one pack, and packs that are closed or are without a path are not counted.
-
Overall ReadHits/Requests
The percentage of cache requests that were read hits.
-
Cache Size
The size of the disk cache. Mwords indicates that the size is in megawords.
-
Reqs/Sec
The average number of cache requests per second.
-
Kbytes/Sec
The average number of kilobytes per second requested by cache requests.
Unit Statistics
The rest of the displayed information is unit statistics. In order for a unit to be included in the display, at least one cache request must have been entered for that unit during the preceding time interval. Inactive units and noncached units are not included in this display.
-
Reqs/Sec
The average number of cache requests for this unit per second.
-
% Rhit/Read
The percentage of read requests for this unit that were read hits.
-
% Read/All
The percentage of all requests for this unit that were reads.
-
% Rhit/All
The percentage of all requests for this unit that were read hits. This column is always equivalent to the product of the previous two columns.
-
Kbytes/Sec
The average number of kilobytes per second requested by cache requests for this unit.
Example 2
This example turns on caching for disk pack 149:
CACHE + PK149
PK 149 CACHING STARTED
Example 3
This example turns off caching for disk pack 149:
CACHE - PK149
PK 149 CACHING STOPPED
Example 4
This example resizes cache memory to 16 megawords:
CACHE MEMORY 16 MWORDS
CACHE MEMORY WILL BE RESIZED
CACHE MEMORY RESIZED TO 16 MWORDS