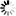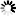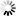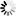The ARCCONVERT command converts the current archive for a family from version 391 to version 531. A version 531 archive directory has approximately four times the capacity of a version 391 archive directory.
When you enter the ARCCONVERT command, the system starts a visible independent runner named COPYDIR. The COPYDIR job immediately changes its name to "ARCCONVERT <family name> (531)".
Syntax
Explanation
ARCCONVERT <family name> VERSION = 531
The system creates a new version 531 archive directory for the family and copies all the records from the existing version 391 archive directory to the new directory. When finished, the system changes the name of the old archive directory to
*OLD/ARCHIVE/<family name>/<nnn> ON <catalog family>
When you issue the ARCCONVERT command, the designated family must already have an active version 391 archive directory running.
You can use the OL PK <unit number> command on the base pack of a family to determine the archive version it is using.
The archive version appears on the same line in the display as the family header version. If there are duplicate or triplicate copies of the active archive directory, you must remove the duplicates before you can use the ARCCONVERT command. Use the ARCDUPLICATE − ON <family name> (<family index>) command to remove the duplicates. After the conversion finishes, you can establish duplicate copies of the new archive directory with the ARCDUPLICATE ON <family name> (<family index>) command.
Considerations for Use
The archive directory conversion process takes approximately three times as long as an archive rebuild to complete. The actual time depends on the size of the original archive directory.
The conversion process blocks all access by other programs to the archive directory and SYSTEMDIRECTORY for the family. Programs that try to use either of these directories must wait for the conversion to finish, but the programs do not show in the waiting mix list. During the conversion, the system rejects requests to use certain commands. For instance, the PD (Print Directory) command might be rejected even if the command is directed to a different family.
The conversion process takes place in three phases. During the first phase, the system copies records from the original archive directory to the new archive directory and issues ongoing progress messages. If any fatal errors occur, or if you use the DS (Discontinue) command to terminate the process, the system reverts to using the original archive directory. At the end of the first phase, the system issues a message indicating how many archive records it copied.
During the second phase, the system deletes all in-use space for the available table in the new archive directory.
During the third phase, the system rebuilds the Archive Access Structure Table (AAST) for the new directory, issues ongoing progress messages, and reports any records with duplicate file names. For these duplicates, the system keeps the record with the most recent timestamp and deletes the other one.
Finally, the system changes the name of the original archive directory and locks the new directory into the SYSTEMDIRECTORY for the catalog family. If you halt/load the system before the name change, the system reverts to using the original archive directory. You can use the ARCCOPY command to make a backup copy of the version 391 archive directory before you use the ARCCONVERT command.
If something goes wrong with the new 531 version of the archive directory, you can use the ARCREPLACE (Replace Archive Directory) command to restore that backup copy of the directory.
The new archive directory uses more disk space on the base pack of the catalog family than the existing 391 version of the directory. You can determine how many areas the active system archive directory uses with the PD (Print Directory) command:
PD SYSTEM/ARCHIVE/<family name>/<family index> ON <catalog family>
You can determine the family name of the catalog family to use in the PD command by issuing the DL (Disk Location) command. You can determine the family index of the base pack of the catalog family to use in the PD command by issuing the PER PK or OL PK <unit number> command.
The PD display shows
TOTAL SECTORS <number> (<number> PER AREA)
To determine the number of areas that the new directory needs, divide the total-sectors number by the sectors-per-area number. If the sectors-per-area number is 4000, then double the number of areas you calculated. Finally, add 2 to the number of areas you calculated. The new archive directory will have 2048 sectors per area. Use the DU (Disk Utilization) command to determine whether there is enough disk space for the new directory:
DU ON <catalog family name> (<base pack family index>) 2048
Check the line of the display that says
<number> areas of 2,048 sectors could be allocated
If the number is less than the number of areas you calculated, then you need to make space available on the base pack of the catalog family before you can use the ARCCONVERT command.