The MQ (Make or Modify Queue) command creates a job queue, changes the attributes of a job queue, or deletes a job queue.
Every job queue has several attributes. When selecting jobs to enter the mix, the CONTROLLER program considers them in order of priority. Queue attributes provide constraints that affect the way jobs are assigned to queues and selected for execution.
If an MQ command does not specify a value for every queue attribute, only the values of the specified attributes are changed or initialized. If a new job queue is being created, unspecified attributes are assigned default values as described in the following text.
All job queues in existence before a halt/load continue to exist and maintain attributes through the halt/load. Jobs that do not have a class specified and are not affected by a unit queue assignment are placed in the default queue. If, however, the CONTROLLER compile-time option QFACTMATCHING is set, those jobs are placed in the highest numbered queue that accepts their attributes.
For more information about job queue processing, refer to the PQ (Purge Queue), QF (Queue Factors), SQ (Show Queue), and UQ (Unit Queue).
Syntax
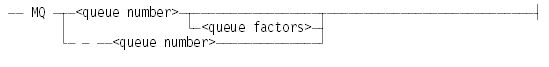
<queue factors>

<queue attributes>
<limits>
<family specification>
<tape specification>

Explanation
MQ <queue number>
Makes a queue with the specified queue number. The highest queue number allowed is 1023. No more than 1024 queues can exist at one time.
MQ − <queue number>
Eliminates the queue from the system. If the queue contains any active entries, the message QUEUE HAS ACTIVE JOBS appears and the queue is not deleted. (If the queue was deleted, and a halt/load occurred before an active job terminated, the job would be impossible to restart after the halt/load because the queue from which it started would no longer exist.) If the queue contains any waiting jobs, they are moved to another queue, if possible, or discontinued if no suitable queue exists.
MQ <queue number> <queue attributes>
Specifies new values for attributes of the specified queue. Attributes can be deleted from the queue, which returns them to the value they would have had if they had never been specified. For example, to delete the FAMILY attribute, specify FAMILY. (you must include the period). To delete the tape resource attributes, specify TAPE0. To delete all other attributes, specify <attribute> –.
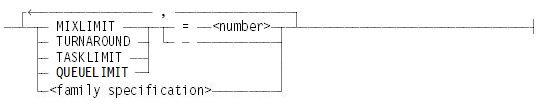
MIXLIMIT = <number>
Assign <number> as the value of the MIXLIMIT attribute. This value is used by the CONTROLLER when selecting jobs from the queues. If the number of scheduled and running jobs (and associated tasks) in the mix that originate from this queue is greater than or equal to the MIXLIMIT value of the queue, the CONTROLLER does not take any more jobs into the mix from the queue.
After a halt/load, the MIXLIMIT for all queues is set to 0 (zero) if the run-time operating system option AUTORECOVERY is reset.
TURNAROUND = <real number>
Assigns <real number> as the value of the TURNAROUND attribute, where <real number> is an unsigned real constant indicating minutes. This value is used by the CONTROLLER when selecting jobs from the queues. Turnaround time is the time since the selection of the previous job from a queue. If that time is greater than the value of the TURNAROUND attribute of the queue, the CONTROLLER favors the queue—unless the value of the TURNAROUND attribute of another queue is exceeded by a greater amount. If no TURNAROUND value is assigned, turnaround time for the queue is assumed not to be a concern and is not computed.
TASKLIMIT = <number>
Assigns <number> as the value of the TASKLIMIT attribute, where <number> is in the range 0 through 31. This attribute limits the number of descendants that a job can have. The limit applied is cumulative. That is, it limits the total number of descendants that a job can have during its history, not just the number of descendants a job can have at the same time.
QUEUELIMIT = <number>
Assigns <number> as the value of the QUEUELIMIT attribute. This value is used by CONTROLLER to limit the number of jobs in a queue. When the QUEUELIMIT is reached, any new jobs are rejected with the following message:
QUEUELIMIT EXCEEDED
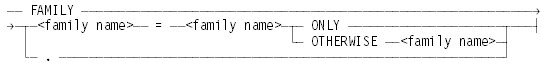
FAMILY <family name> = <family name> ONLY
FAMILY <family name> = <family name> OTHERWISE <family name>
Associate family specifications with a job queue so that default specifications are provided for jobs in that queue. If a queue has a family specification, the family statement is used for any job or user that runs through the queue. If a job has a family statement that does not exactly match the family statement of the queue, the job is rejected by the following message:
QUEUE FAMILY MISMATCH
A user who has a family statement specified in the USERDATAFILE must also exactly match the family statement of the queue to run anything through that queue.
FAMILY.
Removes family specifications from the specified queue.
DEFAULTS
Specifies the default system usage limits that are assigned to jobs selected from that queue. These defaults can be overridden by limit statements placed in the job.
LIMITS
Specifies the maximum system usage limits that the control statements of a job can specify and still be accepted as an entry in that job queue. Thus, if a job specifies larger estimates than the LIMITS values for the desired queue, it is not admitted to the queue and a message is displayed. You should usually specify DEFAULTS whenever you specify LIMITS; otherwise, jobs that do not contain an explicit usage limit statement are not subject to the limits specified in the MQ command. If you set a lower LIMITS value than the DEFAULTS value for the same queue attribute, the system automatically reduces the DEFAULTS value to the specified LIMITS value.
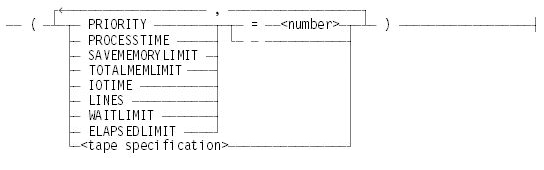
The options described in the following paragraphs specify system usage limits and can be specified for both the DEFAULTS and the LIMITS queue attributes. The exception is the tape specification, which applies to LIMITS only. For each option, the equal sign (=) can be omitted.
PRIORITY = <number>
Assigns <number> as the value of the PRIORITY attribute, where <number> falls in the range 0 through 99. The value of this attribute is the priority to be assigned to a job when it is entered in the mix. Changes to this value can result in all jobs in the queue being requeued (possibly into other queues) at the time the command is issued.
IOTIME = <number>
Assigns <number> as the value of the MAXIOTIME attribute, where <number> is in units of seconds. The value of this attribute is the maximum input/output (I/O) time to be allowed when the job is executed. If this option is not specified, an unlimited amount of job I/O time is allowed by default.
PROCESSTIME = <number>
Assigns <number> as the value of the MAXPROCESSTIME attribute, where <number> is in units of seconds. The value of this attribute is the maximum processor time to be allowed when the job is executed. If this option is not specified, an unlimited amount of job processor time is allowed by default.
LINES = <number>
Assigns <number> as the value of the MAXLINES attribute. The value of this attribute is the maximum number of lines of printed output that can be generated by the execution of the job. If this option is not specified, an unlimited number of lines are allowed by default.
WAITLIMIT = <number>
Specifies <number> as the value for the WAITLIMIT attribute, where<number> is in units of seconds. This attribute specifies the maximum amount of time that a task waits for an event.
ELAPSEDLIMIT = <number>
Specifies <number> as the value for the ELAPSEDLIMIT attribute, where <number> is in units of seconds. The value of this attribute is the maximum time that a job can be active in the system.
SAVEMEMORYLIMIT = <number>
Specifies <number> as the value of the SAVEMEMORYLIMIT attribute, where <number> is in units of words. The value of this attribute is the maximum amount of memory a task can allocate to save.
TOTALMEMLIMIT = <number>
Specifies <number> as the value of the TOTALMEMLIMIT attribute, where <number> is in units of words. The value of this attribute is the maximum amount of memory a task can allocate.
<tape specification>
Specifies the following values:
-
The maximum number of tape units a job can specify in a RESOURCE task attribute specification
-
The maximum number of tape units that a task within the job can specify in a RESOURCE task attribute
The system enforces this limit only when the RESOURCECHECK option is set. TAPE0 nullifies the resource limits for all tape types and reestablishes unrestricted use of all tape resources.
| Note: | This attribute can be used only when LIMITS is specified; it cannot be used with DEFAULTS. |
Examples
Example 1
This example makes a queue with a queue number of 37, a MIXLIMIT of 2, and no DEFAULTS or LIMITS system usage specifications:
MQ 37 ML = 2
QUEUE 37:
MIXLIMIT = 2
DEFAULTS:
NONE
LIMITS:
NONEExample 2
This example creates a queue, numbered 4, with the specified attributes:
MQ 4 MIXLIMIT=3, TURNAROUND=2.5, DEFAULTS(PRIORITY=60, IOTIME=20,PROCESSTIME=3,LINES=50),LIMITS (PRIORITY=80,IOTIME=60,PROCESSTIME=20,LINES=200, TAPE=14)
QUEUE 4:
MIXLIMIT = 3
TURNAROUND = 2.50
DEFAULTS:
PRIORITY = 60
PROCESSTIME = 3
IOTIME = 20
LINES = 50
LIMITS:
PRIORITY = 80
PROCESSTIME = 20
IOTIME = 60
LINES = 200
RESOURCE:
TAPE = 14Example 3
This example causes all jobs in queue 5 without a FAMILY specification to be assigned a family specification of DISK=STUDENTFILES OTHERWISE DISK, and jobs with a FAMILY specification other than DISK=STUDENTFILES OTHERWISE DISK to be denied entry into queue 5.
MQ 5 FAMILY DISK = STUDENTFILES OTHERWISE DISK