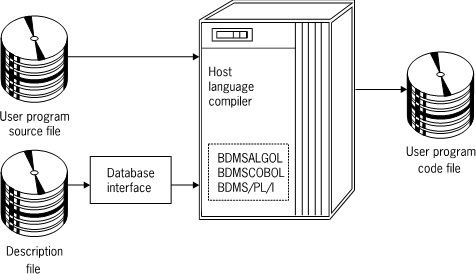
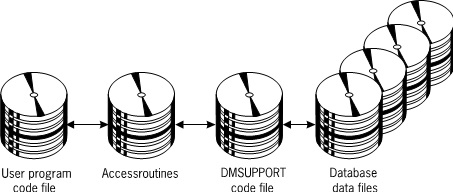
The Enterprise Database Server provides you with two alternatives for programming interfaces to the database: through language extensions and through an interpretive interface. User Program Compilation shows how a user program is compiled, and User Program Execution shows how a user program is executed.
Language Extensions
User programs written in ALGOL, COBOL74, COBOL85, or RPG can access an Enterprise Database Server database using data management statements implemented in those languages. All data management statements are incorporated in the compilers for the host languages; therefore, there is no need to preprocess these statements as in other database management systems.
Each data management statement executed by a user program invokes a portion of the Accessroutines to perform all of the file management functions required by the statement. Using the Accessroutines in this way enables the user programmer to concentrate on the application, rather than the burdens of file resource management, key conversions, and other file management responsibilities inherent in handling conventional files.
Interpretive Interface
The interpretive interface uses the standard language compiler as its compile-time interface and the Accessroutines as its run-time interface. The standard language compiler produces the object code file for your application program. At run time, the application program accesses the interpretive interface that in turn uses the Accessroutines to manipulate the database. This arrangement allows for application programs that are not dependent on any particular database description. This arrangement also means that
-
A single application program, through the library mechanism, can invoke as many databases as desired. (A Database Interpreter library must be compiled for each database.)
-
You can create general-purpose programs that can access any database.
-
Decisions about database operations can be postponed until runtime.