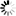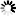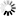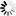── ACCESS ─┬───────────────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────┤
├─ . ───────────────────────────────────────┤
└─<accesscode>─┬────────────────────────────┤
├─ . ────────────────────────┤
├─────┬─<acesscode password>─┘
└─ / ─┘<accesscode>
──<name>───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
<accesscode password>
──<password>───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
Explanation
The ACCESS command is used to interrogate or change the accesscode of a session.
When ACCESS is entered, the current accesscode for the session is returned (not including the accesscode password).
The ACCESS form assigns a null accesscode to the session. If the ACCESSCODENEEDED attribute is set in the USERDATAFILE for the usercode, the request is denied.
The ACCESS <accesscode>/<apassword> form assigns or change the session's accesscode and corresponding accesscode password after validation in the USERDATAFILE. The ACCESS command does not alter the USERDATAFILE. If the <apassword> is not supplied, it is requested.
The ACCESS <accesscode> form is used when no accesscode password exists for a particular accesscode.
On systems with the Secure Access Control Module or Password Management security packages, the accesscode password must be entered on a separate line (and usually in a protected field), if the security option SECUREPASSWORDS is set.
Changes of accesscodes to a session are logged.
| Note: | If the CASESENSITIVEPW security option is set, passwords must be entered in a case-sensitive form. |
For additional information on accesscodes, refer to User Identification and Logging On.
Examples
ACCESS #ACCESSCODE = CODE1. ACCESS CODE/PASS #SESSION 4094 ET=8:10.1 PT=1:08.9 IO=3.4.1 #CONTINUE SESSION 4094 13:32:47 10/17/83 #ACCESSCODE = CODE.