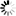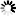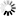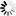── LIST ─┬─<specified file>─┬───────────────────────────────────┤
└─<work file>──────┘<specified file>
┌◄────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
──┴─┬─/1*\─<file title>───────────────────────────┬─┴──────────────────┤
├─/1\─┬─<sequence range list>─────────────────┤
│ └─<sequence number>── FOR ──<integer>───┤
├─/1\─ @ ──<start column>─┬───────────────────┤
│ └─ - ──<end column>─┤
└─/1\─<altered records options>───────────────┘<altered records options>
┌◄──────── , ───────┐
── : ─┴─┬─ A ───────────┬─┴────────────────────────────────────────────┤
├─ AF ──────────┤
├─ AFN ─────────┤
├─ AN ──────────┤
├─ ANF ─────────┤
├─ CHANGES ─────┤
├─ COMPARE ─────┤
├─ FLAG ────────┤
├─ PAGEFORMAT ──┤
├─ SQUASHED ────┤
├─ TRUNCATED ───┤
└─ UNSEQUENCED ─┘<work file>
┌◄────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
──┴─┬─────────────────────────────────────────────┬─┴──────────────────┤
├─/1\─┬─<sequence range list>─────────────────┤
│ ├─<sequence number>── FOR ──<integer>───┤
│ └─<current line handling>───────────────┤
├─/1\─ @ ──<start column>─┬───────────────────┤
│ └─ - ──<end column>─┤
└─/1\─<altered records options>───────────────┘<current line handling>
──┬─ = ─────────────┬─┬──────────────────┬─┬───────────────────────────┤ ├─ > ─┬─<integer>─┘ └─ FOR ──<integer>─┘ │ ├─ < ─┘ │ └─<sequence number>── = ─────────────────┘
Explanation
The LIST command displays the contents of a work file or other specified file at the station. If a file title is not specified, the contents of the work file are listed. If a file title is specified, the file is listed provided that the user has access privileges.
Listing a Specified File
The LIST command displays a file other than the work file if a file title is specified. If the user has sufficient file access privileges, the specified file need not be limited to the user's files.
LIST <sequence range list>
A sequence range list in the command indicates that only the records in the specified sequence range are to be listed.
LIST <sequence number> FOR <integer>
The LIST <sequence number> FOR <integer> form of the command lists a specified number of lines starting from the sequence number. The FOR <integer> construct specifies the total number of lines to be listed. If the number of lines from the sequence number to the end of the file is less than the specified integer, the LIST option displays the number of lines available in the file. If the integer specified is 0 (zero) or 1, then the sequence number is listed. If the sequence number does not exist in the file, the list starts with the next higher sequence number, if any.
LIST @ <start column> LIST @ <start column>-<end column>
The @ <start column> option lists records beginning from the specified start column. The LIST @ <start column> – <end column> form of the command can be used to indicate that only the specified range of columns of each record are to be listed. The start column and end column values must be integers, the end column value cannot be less than the start column value, and both the start column and the end column values must be within the text field of the file.
Altered Records Options
The following LIST options are used to list alterations that have been made to the work file by FIX, DELETE, and single-line entry since the work file was last updated. (An update is performed when an UPDATE command is entered or when an update is forced by the MERGE, RMERGE, EXCLUDE, INSERT, MOVE, RESEQ, COMPILE, EXECUTE, TYPE, REPLACE, UTILITY, or SAVE command. Under certain conditions, issuing the LIST command with a sequence range or FOR part causes an update to occur if the listed file is the current work file. For details, refer to “Listing a Work File” later in this section.)
A
The A option lists only altered lines in the work file. The original version of each line that has been deleted by a DELETE command or changed by a single-line entry is listed and flagged with a minus sign (–). The original versions of lines modified by the FIX command are not listed.
New lines of text are flagged as follows:
-
For an old line replaced by a new line, the flag is an R.
-
For a new line inserted, the flag is an I.
-
Each line that has been modified by the FIX command is listed and flagged with an F.
Blank lines are inserted to separate the listing into groups; a group contains the original version of a line of text (except for lines changed by the FIX command) followed by the changed, replaced, or inserted line of text. Consecutively inserted or deleted lines are shown as a single group.
AF
The output from the AF option is the same as the A option output, except that the original version of lines changed by the FIX command are also displayed. The line showing the record before the FIX command was transmitted is flagged with a minus sign (–). (This option is functionally equivalent to the COMPARE option.)
AN
The output for the AN option is the same as the A option output, except that the neighboring lines of a new line are listed and are not flagged.
AFN, ANF
The AFN option combines the effects of the AN and AF options. Lines are shown before fixing, and the neighbors of new lines are shown. AFN and ANF are synonymous.
CHANGES
The output for the CHANGES option is the same as the A option output, except that only the sequence numbers (not the text) of deleted lines appear in the list, and groups of altered lines are not separated by vertical lines.
COMPARE
The COMPARE option lists only altered lines in the work file. The original version of each line that has been deleted by the DELETE command, or changed by a single-line entry or a FIX command is listed and flagged with a minus sign (–). New lines of text are flagged as follows:
-
For an old line replaced by a new line, the flag is an R.
-
For a new line inserted, the flag is an I.
-
Each line that has been modified by the FIX command is listed and flagged with an F.
Blank lines are inserted to separate the listing into groups; a group contains the original version of a line of text followed by the fixed, replaced, or inserted line of text. Consecutively inserted or deleted lines are shown as a single group. The COMPARE option is functionally equivalent to the AF option.
FLAG
The FLAG option causes each line in the work file to be listed with the altered lines flagged as described for the A option. Groups of altered lines are not separated by vertical spaces.
Format Options
Several output format options are available with the LIST command. If no format option is specified, the default format is used; that is, the sequence number of the line appears (pseudo-sequence numbers for type data files) with leading zeros omitted, followed by a blank and the text of the line. Lines too long for the terminal are split (on token boundaries where possible). All lines that have been marked with a current MARKID are displayed with an asterisk (*) between the sequence number and the rest of the line, as long as the PAGEFORMAT, and UNSEQUENCED options are not in effect. For more information on the MARKID, refer to the GET, MAKE, and MARKID commands. The format options and their effects are described in the following paragraphs.
PAGEFORMAT
The PAGEFORMAT option causes the output to appear in a format similar to the page mode output. That is, the full length of the sequence number field is displayed, immediately followed by the contents of the text field (the blank or asterisk flag character is omitted).
SQUASHED
The SQUASHED option causes any group of multiple blanks to be reduced to a single blank.
TRUNCATED
The TRUNCATED option causes the output line to be truncated if the width of the CANDE station is less than the MAXRECSIZE of the work file. (The backslash character (\) designates the character position at which truncation takes place.)
UNSEQUENCED
The UNSEQUENCED option causes the lines to be listed without sequence numbers.
Listing a Work File
If a file title is not specified in the LIST command, the user's work file is displayed as specified by the LIST options. The LIST options for a work file are identical to those for a specified file, except that they include the added feature of listing lines of the work file from the current line.
If a sequence range is specified in the LIST command, CANDE might update the work file before displaying the correct number of lines. CANDE updates the work file if the following types of changes are made to the work file:
-
A single line deletion on the work file
-
Multiple line deletions on the work file
Issuing the LIST command again with a sequence range does not result in an update of the work file. The LIST command updates the work file again only if additional changes are made to the work file by deleting a single line or multiple lines from the work file.
<current line handling>
The current line of the work file is defined as one of the following:
-
The line that was last entered.
-
The line that was last modified with the FIX command.
-
The line that was specified through the LIST command that sets the current line. For example, line 800 is the current line if the following form of the LIST command is used:
LIST 800 =
The last action entered determines the current line. The concept of the current line and the LIST options for manipulating the current line apply only to editing work files.
LIST =
The LIST = form of the command lists the current line of the work file.
LIST > <integer>
LIST> <integer> FOR <integer>
The LIST > <integer> form of the command moves the file forward the number of lines specified from the current line and displays that line number. The new line becomes the current line. The FOR <integer> option displays the number of lines specified after the new current line.
LIST < <integer>
LIST < <integer> LIST < <integer> FOR <integer>
The LIST < <integer> form of the command moves the file backwards the number of lines specified from the current line and displays that line number. The new line becomes the current line. The FOR <integer> option displays the number of lines specified after the new current line.
Examples
l 100 BEGIN 200 REAL Y; 300 Y:=2; 400 END. # LIST (UZER)FILE ON USERPACK 200-400 72-80 #FILE (UZER)FILE ON USERPACK 200 THIS IS 300 COMMENT 400 SECTION #
The following example lists ten lines starting at line 1500:
LIST 1500 FOR 10
The following example lists 21 lines starting at line 200100:
L 200100 F 21
The following example lists four lines that have the current MARKID:
L 40-70 40*Now is the time 50*for all good people 60*to come to the aid 70*of their country. #
The following example lists the full sequence number field followed by the contents of the text fields:
LIST 1,999000:PA 00000001This is my very first line 00999000... and this is the last
The following examples demonstrate the use of the LIST command when working with a work file:
L 100 Line 1 200 Line 2 300 Line 3 400 Line 4 500 Line 5 600 Line 6 700 Line 7 # L 400 = 400 Line 4 FIX = .4.4mod # L = 400 Line 4mod # L > 2 FOR 2 600 Line 6 700 Line 7 # L = 600 Line 6 # L < 3 FOR 3 300 Line 3 400 Line 4mod 500 Line 5 #