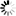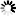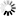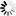── CONNECT ─┬───────────────────────┬─ TO ──<host specification>───────►
└─ [ ──< protocol>── ] ─┘
►─┬─────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────┤
└─ : ─┬─<MCS name>────┤
└─<port number>─┘<host specification>
──┬─<host name>───┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤ ├─<IP address>──┤ └─<domain name>─┘
<protocol>
──┬─ STAXFER ────────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────┤
└─ TELNET ─┬───────────────────────────┤
└─┬─────┬─────┬─ SSL ───────┤
└─ , ─┘ ├─ TSL ───────┤
└─ SECURE ────┘<MCS name>
──<file title>─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
<port number>
──<number>─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
Explanation
The CONNECT command allows you to transfer control of a data comm station from the MCS of the local host to an MCS on a remote host. The transfer is performed by Host Services Station Transfer or by Telnet. Once the logical connection is established between the station and the remote MCS, the station behaves as if it were actually connected to the remote host.
The CONNECT command initiates a station transfer dialog between the local host and the host specified in the host specification.
If the usercode attribute NOSTATIONXFER is TRUE, you cannot use the CONNECT command to transfer control to an MCS on a remote host.
| Note: | An MCS name is only used when the station is transferred using Host Services Station Transfer and a port number is only used when the station is transferred using Telnet. |
You can specify the connection protocol to be used. STAXFER indicates a BNA Station Transfer and TELNET indicates a TCP/IP Telnet connection. The TELNET SSL/TLS/SECURE specification indicates that the TELNET connection should be made over a secured port. If you do not specify the connection protocol, the Station Transfer MCS determines the protocol to be used. The TELNET connection protocol must be compatible with the SECURECOMM TELNET security option; however, if the SSL/TLS/SECURE specification is not included and the option is set to REQUIRED, a secure connection will be attempted.
If you specify the connection protocol, it must be compatible with the host specification. A BNA station transfer requires a BNA host name, and a Telnet connection requires a TCP/IP host name, domain name, or IP address.
You can make a logical connection to a remote host by specifying either a host name, an IP address that identifies a host, or a domain name that identifies a host system.
The host name identifies the remote host in a BNA or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network. The host name can contain from 1 to 17 alphanumeric characters.
An IP address is a numerical designator that uniquely identifies a host within a specific local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN) that forms part of an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
An IP address can be either an IPv4 address or an IPv6 address. For additional information on IP address format, refer to the “IPv6 and IPv4 Common Utilities” section in MCP System Interfaces Programming Reference Manual.
A domain name is a map used for routing queries related to message routing in an IP network. A domain name uniquely identifies a host system or host-dependent entity in terms of the local tree structure that defines the domain name space. On ClearPath systems, a domain name can be as many as 255 bytes in length and can consist of alphanumeric, hyphen (-), and underscore (_) characters.
MCS Name Option
If you provide an MCS name, the station is transferred to the specified MCS on the remote host. The MCS name is ignored if the station transfer is performed by Telnet. The station transfer will fail if the MCS name is different from the default MCS on the remote host and if the default MCS has been restricted using the ONLY option of the DEFAULT MCS Station Transfer command. If you do not specify MCS name, the station is transferred to the default MCS of the remote host.
If the specified MCS is not running, an attempt is made to start it when the station is transferred to it. Once the station is transferred to the remote MCS, the MCS might require you to log on with a valid usercode and password for that host.
Port Number
The Port Number indicates the remote port number to be used when making a Telnet connection to a host in a TCP/IP network. If none is specified, port 23, the default Telnet port, is used.
Initiating a Station Transfer Dialog
The BNA network must be running at the local host before a Host Services Station Transfer dialog can be initiated.
Examples
CONNECT TO HOSTA CONNECT TO HOSTB: SYSTEM/CANDE CONNECT [TELNET, SSL] TO SOMETCPHOST CONNECT [TELNET SECURE] TO SOMETCPHOST